

Next: About this document ...
Up: ESMC_crefdoc
Previous: Bibliography
Contents
Subsections
33 Appendix A: Master List of Constants
This flag is documented in section 26.2.1.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.1.
33.3 ESMC_DECOMP
DESCRIPTION:
Indicates how DistGrid elements are decomposed over DEs.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_Decomp_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_DECOMP_BALANCED
- Decompose elements as balanced as possible across DEs. The maximum
difference in number of elements per DE is 1, with the extra elements on
the lower DEs.
- ESMC_DECOMP_CYCLIC
- Decompose elements cyclically across DEs.
- ESMC_DECOMP_RESTFIRST
- Divide elements over DEs. Assign the rest of this division to the first
DE.
- ESMC_DECOMP_RESTLAST
- Divide elements over DEs. Assign the rest of this division to the last DE.
- ESMC_DECOMP_SYMMEDGEMAX
- Decompose elements across the DEs in a symmetric fashion. Start with the
maximum number of elements at the two edge DEs, and assign a decending
number of elements to the DEs as the center of the decomposition is
approached from both sides.
type(ESMC_ExtrapMethod_Flag)
DESCRIPTION:
Specify which extrapolation method to use on unmapped destination points after
regridding.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_ExtrapMethod_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_EXTRAPMETHOD_NONE
- Indicates that no extrapolation should be done.
- ESMC_EXTRAPMETHOD_NEAREST_STOD
- Inverse distance weighted average.
Here the value of a destination point is the weighted average of the
closest N source points. The weight is the reciprocal of the distance of
the source point from the destination point raised to a power P. All the
weights contributing to one destination point are normalized so that they
sum to 1.0. The user can choose N and P when using this method, but
defaults are also provided.
- ESMC_EXTRAPMETHOD_NEAREST_IDAVG
- Nearest source to destination.
Here each destination point is mapped to the closest source point. A given
source point may go to multiple destination points, but no destination
point will receive input from more than one source point.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.6.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.2.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.3.
33.7 ESMC_INDEX
DESCRIPTION:
Indicates whether index is local (per DE) or global (per object).
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_IndexFlag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_INDEX_DELOCAL
- Indicates that DE-local index space starts at lower bound 1 for each DE.
- ESMC_INDEX_GLOBAL
- Indicates that global indices are used. This means that DE-local index
space starts at the global lower bound for each DE.
- ESMC_INDEX_USER
- Indicates that the DE-local index bounds are explicitly set by the user.
33.8 ESMC_LINETYPE
DESCRIPTION:
This argument allows the user to select the path of the
line which connects two points on the surface of a sphere.
This in turn controls the path along which distances are calculated and the
shape of the edges that make up a cell.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_LineType_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_LINETYPE_CART
- Cartesian line. When this option is specified distances are calculated in a
straight line through the 3D Cartesian space in which the sphere is
embedded. Cells are approximated by 3D planes bounded by 3D Cartesian lines
between their corner vertices.
When calculating regrid weights, this line type is currently the default for
the following regrid methods: ESMC_REGRIDMETHOD_BILINEAR,
ESMC_REGRIDMETHOD_PATCH, ESMC_REGRIDMETHOD_NEAREST_STOD, and
ESMC_REGRIDMETHOD_NEAREST_DTOS.
- ESMC_LINETYPE_GREAT_CIRCLE
- Great circle line. When this option is specified distances are calculated
along a great circle path (the shortest distance between two points on a
sphere surface). Cells are bounded by great circle paths between their
corner vertices. When calculating regrid weights, this line type is
currently the default for the following regrid method:
ESMC_REGRIDMETHOD_CONSERVE.
This flag is documented in section 31.2.1.
This flag is documented in section 31.2.2.
This flag is documented in section 20.2.1.
33.12 ESMF_METHOD
DESCRIPTION:
Specify standard ESMF Component method.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMF_Method_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMF_METHOD_FINALIZE
- Finalize method.
- ESMF_METHOD_INITIALIZE
- Initialize method.
- ESMF_METHOD_READRESTART
- ReadRestart method.
- ESMF_METHOD_RUN
- Run method.
- ESMF_METHOD_WRITERESTART
- WriteRestart method.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.4.
33.14 ESMC_REDUCE
DESCRIPTION:
Indicates reduce operation.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_Reduce_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_REDUCE_SUM
- Use arithmetic sum to add all data elements.
- ESMC_REDUCE_MIN
- Determine the minimum of all data elements.
- ESMC_REDUCE_MAX
- Determine the maximum of all data elements.
33.15 ESMC_REGION
DESCRIPTION:
Specifies various regions in the data layout of an Array or Field object.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_Region_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_REGION_TOTAL
- Total allocated memory.
- ESMC_REGION_SELECT
- Region of operation-specific elements.
- ESMC_REGION_EMPTY
- The empty region contains no elements.
This flag is documented in section 16.2.1.
This flag is documented in section 19.2.5.
33.18 ESMC_TYPEKIND
DESCRIPTION:
Named constants used to indicate type and kind combinations supported by the
overloaded ESMC interfaces. The corresponding Fortran kind-parameter constants
are described in the ESMF_TYPEKIND section of Appendices of the ESMF Fortran
reference manual.
The type of these named constants is:
type(ESMC_TypeKind_Flag)
The named constants are:
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_I1
- Indicates 1 byte integer.
(Only available if ESMF was built with
ESMF_NO_INTEGER_1_BYTE = FALSE. This is not the default.)
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_I2
- Indicates 2 byte integer.
(Only available if ESMF was built with
ESMF_NO_INTEGER_2_BYTE = FALSE. This is not the default.)
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_I4
- Indicates 4 byte integer.
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_I8
- Indicates 8 byte integer.
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_R4
- Indicates 4 byte real.
- ESMC_TYPEKIND_R8
- Indicates 8 byte real.
33.19 ESMC_UNMAPPEDACTION
DESCRIPTION:
Indicates what action to take with respect to unmapped destination points
and the entries of the sparse matrix that correspond to these points.
The type of this flag is:
type(ESMC_UnmappedAction_Flag)
The valid values are:
- ESMC_UNMAPPEDACTION_ERROR
- An error is issued when there exist destination points in a regridding
operation that are not mapped by corresponding source points.
- ESMC_UNMAPPEDACTION_IGNORE
- Destination points which do not have corresponding source points are
ignored and zeros are used for the entries of the sparse matrix
that is generated.
The schematic below shows the Unified Modeling Language (UML) notation
for the class diagrams presented in this Reference Manual. For
more on UML, see references such as The Unified Modeling Language
Reference Manual, Rumbaugh et al, [2].
35 Appendix C: ESMF Error Return Codes
The tables below show the possible error return codes for Fortran and
C methods.
=====================================
Fortran Symmetric Return Codes 1-500
=====================================
ESMF_SUCCESS 0
ESMF_RC_OBJ_BAD 1
ESMF_RC_OBJ_INIT 2
ESMF_RC_OBJ_CREATE 3
ESMF_RC_OBJ_COR 4
ESMF_RC_OBJ_WRONG 5
ESMF_RC_ARG_BAD 6
ESMF_RC_ARG_RANK 7
ESMF_RC_ARG_SIZE 8
ESMF_RC_ARG_VALUE 9
ESMF_RC_ARG_DUP 10
ESMF_RC_ARG_SAMETYPE 11
ESMF_RC_ARG_SAMECOMM 12
ESMF_RC_ARG_INCOMP 13
ESMF_RC_ARG_CORRUPT 14
ESMF_RC_ARG_WRONG 15
ESMF_RC_ARG_OUTOFRANGE 16
ESMF_RC_ARG_OPT 17
ESMF_RC_NOT_IMPL 18
ESMF_RC_FILE_OPEN 19
ESMF_RC_FILE_CREATE 20
ESMF_RC_FILE_READ 21
ESMF_RC_FILE_WRITE 22
ESMF_RC_FILE_UNEXPECTED 23
ESMF_RC_FILE_CLOSE 24
ESMF_RC_FILE_ACTIVE 25
ESMF_RC_PTR_NULL 26
ESMF_RC_PTR_BAD 27
ESMF_RC_PTR_NOTALLOC 28
ESMF_RC_PTR_ISALLOC 29
ESMF_RC_MEM 30
ESMF_RC_MEM_ALLOCATE 31
ESMF_RC_MEM_DEALLOCATE 32
ESMF_RC_MEMC 33
ESMF_RC_DUP_NAME 34
ESMF_RC_LONG_NAME 35
ESMF_RC_LONG_STR 36
ESMF_RC_COPY_FAIL 37
ESMF_RC_DIV_ZERO 38
ESMF_RC_CANNOT_GET 39
ESMF_RC_CANNOT_SET 40
ESMF_RC_NOT_FOUND 41
ESMF_RC_NOT_VALID 42
ESMF_RC_INTNRL_LIST 43
ESMF_RC_INTNRL_INCONS 44
ESMF_RC_INTNRL_BAD 45
ESMF_RC_SYS 46
ESMF_RC_BUSY 47
ESMF_RC_LIB 48
ESMF_RC_LIB_NOT_PRESENT 49
ESMF_RC_ATTR_UNUSED 50
ESMF_RC_OBJ_NOT_CREATED 51
ESMF_RC_OBJ_DELETED 52
ESMF_RC_NOT_SET 53
ESMF_RC_VAL_WRONG 54
ESMF_RC_VAL_ERRBOUND 55
ESMF_RC_VAL_OUTOFRANGE 56
ESMF_RC_ATTR_NOTSET 57
ESMF_RC_ATTR_WRONGTYPE 58
ESMF_RC_ATTR_ITEMSOFF 59
ESMF_RC_ATTR_LINK 60
ESMF_RC_BUFFER_SHORT 61
ESMF_RC_TIMEOUT 62
ESMF_RC_FILE_EXISTS 63
ESMF_RC_FILE_NOTDIR 64
ESMF_RC_MOAB_ERROR 65
ESMF_RC_NOOP 66
ESMF_RC_NETCDF_ERROR 67
68-499 reserved for future Fortran symmetric return code definitions
=====================================
C/C++ Symmetric Return Codes 501-999
=====================================
ESMC_RC_OBJ_BAD 501
ESMC_RC_OBJ_INIT 502
ESMC_RC_OBJ_CREATE 503
ESMC_RC_OBJ_COR 504
ESMC_RC_OBJ_WRONG 505
ESMC_RC_ARG_BAD 506
ESMC_RC_ARG_RANK 507
ESMC_RC_ARG_SIZE 508
ESMC_RC_ARG_VALUE 509
ESMC_RC_ARG_DUP 510
ESMC_RC_ARG_SAMETYPE 511
ESMC_RC_ARG_SAMECOMM 512
ESMC_RC_ARG_INCOMP 513
ESMC_RC_ARG_CORRUPT 514
ESMC_RC_ARG_WRONG 515
ESMC_RC_ARG_OUTOFRANGE 516
ESMC_RC_ARG_OPT 517
ESMC_RC_NOT_IMPL 518
ESMC_RC_FILE_OPEN 519
ESMC_RC_FILE_CREATE 520
ESMC_RC_FILE_READ 521
ESMC_RC_FILE_WRITE 522
ESMC_RC_FILE_UNEXPECTED 523
ESMC_RC_FILE_CLOSE 524
ESMC_RC_FILE_ACTIVE 525
ESMC_RC_PTR_NULL 526
ESMC_RC_PTR_BAD 527
ESMC_RC_PTR_NOTALLOC 528
ESMC_RC_PTR_ISALLOC 529
ESMC_RC_MEM 530
ESMC_RC_MEM_ALLOCATE 531
ESMC_RC_MEM_DEALLOCATE 532
ESMC_RC_MEMC 533
ESMC_RC_DUP_NAME 534
ESMC_RC_LONG_NAME 535
ESMC_RC_LONG_STR 536
ESMC_RC_COPY_FAIL 537
ESMC_RC_DIV_ZERO 538
ESMC_RC_CANNOT_GET 539
ESMC_RC_CANNOT_SET 540
ESMC_RC_NOT_FOUND 541
ESMC_RC_NOT_VALID 542
ESMC_RC_INTNRL_LIST 543
ESMC_RC_INTNRL_INCONS 544
ESMC_RC_INTNRL_BAD 545
ESMC_RC_SYS 546
ESMC_RC_BUSY 547
ESMC_RC_LIB 548
ESMC_RC_LIB_NOT_PRESENT 549
ESMC_RC_ATTR_UNUSED 550
ESMC_RC_OBJ_NOT_CREATED 551
ESMC_RC_OBJ_DELETED 552
ESMC_RC_NOT_SET 553
ESMC_RC_VAL_WRONG 554
ESMC_RC_VAL_ERRBOUND 555
ESMC_RC_VAL_OUTOFRANGE 556
ESMC_RC_ATTR_NOTSET 557
ESMC_RC_ATTR_WRONGTYPE 558
ESMC_RC_ATTR_ITEMSOFF 559
ESMC_RC_ATTR_LINK 560
ESMC_RC_BUFFER_SHORT 561
ESMC_RC_TIMEOUT 562
ESMC_RC_FILE_EXISTS 563
ESMC_RC_FILE_NOTDIR 564
ESMC_RC_MOAB_ERROR 565
ESMC_RC_NOOP 566
ESMC_RC_NETCDF_ERROR 567
568-999 reserved for future C/C++ symmetric return code definitions
=====================================
C/C++ Non-symmetric Return Codes 1000
=====================================
ESMC_RC_OPTARG_BAD 1000

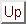


Next: About this document ...
Up: ESMC_crefdoc
Previous: Bibliography
Contents
esmf_support@ucar.edu